COMSOL has the best multiphysical simulation capabilities in my experience. Technical support from Elisa at TECHNIC as well as the engineers at COMSOL has been great.
COMSOL is an important part of our research in plasma physics. We use it in the design of plasma systems and it helps us to obtain a greater understanding of the underlying physics. We have always valued the quick support from TECHNIC and COMSOL and it has been a pleasure to work with them.
Comsol has become a valuable part of our design and decision making process. The exceptional flexibility and access to the physics and solvers in Comsol has allowed us to have deeper understanding on thermomechanical solutions. Technic and Comsol have always been quick and helpful to resolve any issues and provide helpful advice on their products.
At Scion we use COMSOL Multiphysics to understand energy processes, such as the interplay of non-linear solid mechanics and heat & mass transfer during biomass compaction, to design new or more efficient processes.
We use COMSOL Multiphysics to design the customised muffler. With it, we can simulate the insertion loss at different spectrum with different muffler designs.
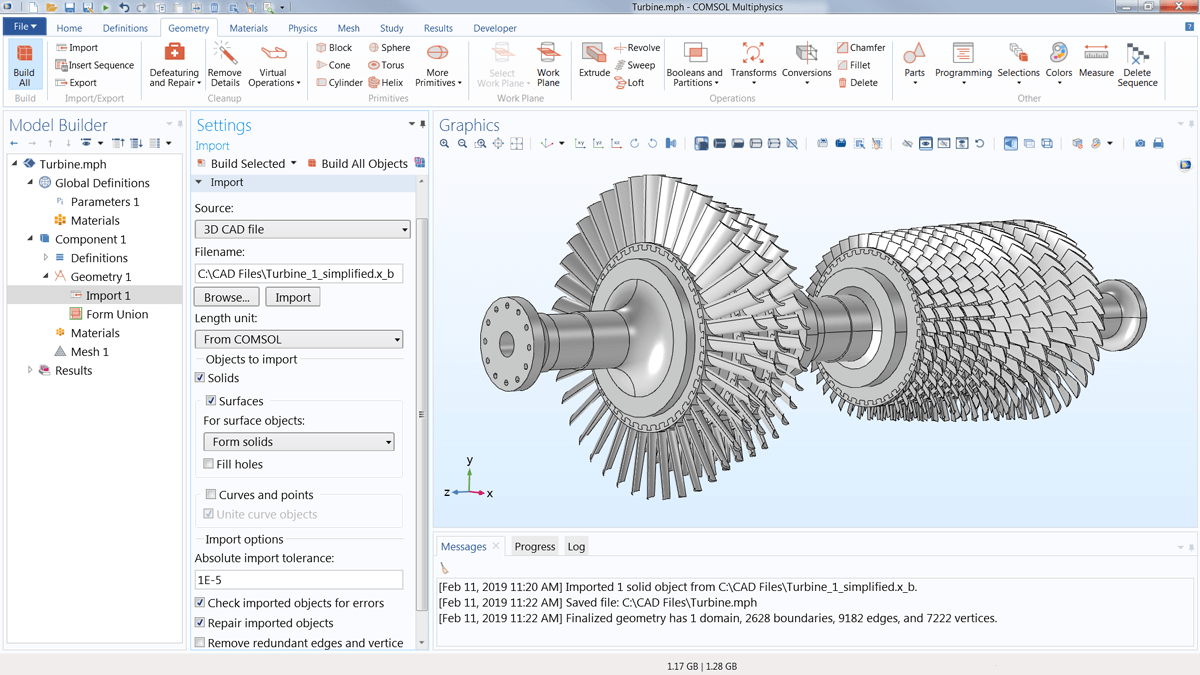
All CAD software supports the export of Parasolid®, ACIS®, STEP, and IGES file formats, which can then be readily imported into COMSOL Multiphysics®. In addition, the CAD Import Module allows you to import the native file formats of a number of CAD systems, such as SOLIDWORKS®, Inventor®, PTC® Creo® Parametric™, NX™, and AutoCAD®. The separate File Import for CATIA® V5 provides support for importing the native file format for this system. When you have installed the CAD Import Module, all CAD files are automatically converted to a Parasolid® geometry using the Parasolid® geometry engine that is included with the module. These geometries can subsequently be changed by the tools within COMSOL Multiphysics® and the CAD Import Module, including, for instance, a conscious change to the geometry. An example of this is creating a model domain around a CAD design, such as an enclosure for use in, for example, a CFD, acoustics, or electromagnetics analysis. Most CAD models are geometries of the objects to be manufactured, and simulation may be used to model the phenomena around this object, such as the flow of air. When these changes have been made, the CAD Import Module can export them in the IGES, STEP, Parasolid® or ACIS® file formats for import into other tools.
Note that not all file formats are supported on all operating systems; for details, see the system requirements.
When running a finite element analysis, cleaning up the geometry for the analysis is just as important as importing the geometry itself. The CAD Import Module contains the necessary tools for repairing geometry that inherits errors upon transfer, defeaturing geometry that is overly detailed, and removing geometric entities that cause unnecessarily fine meshes.
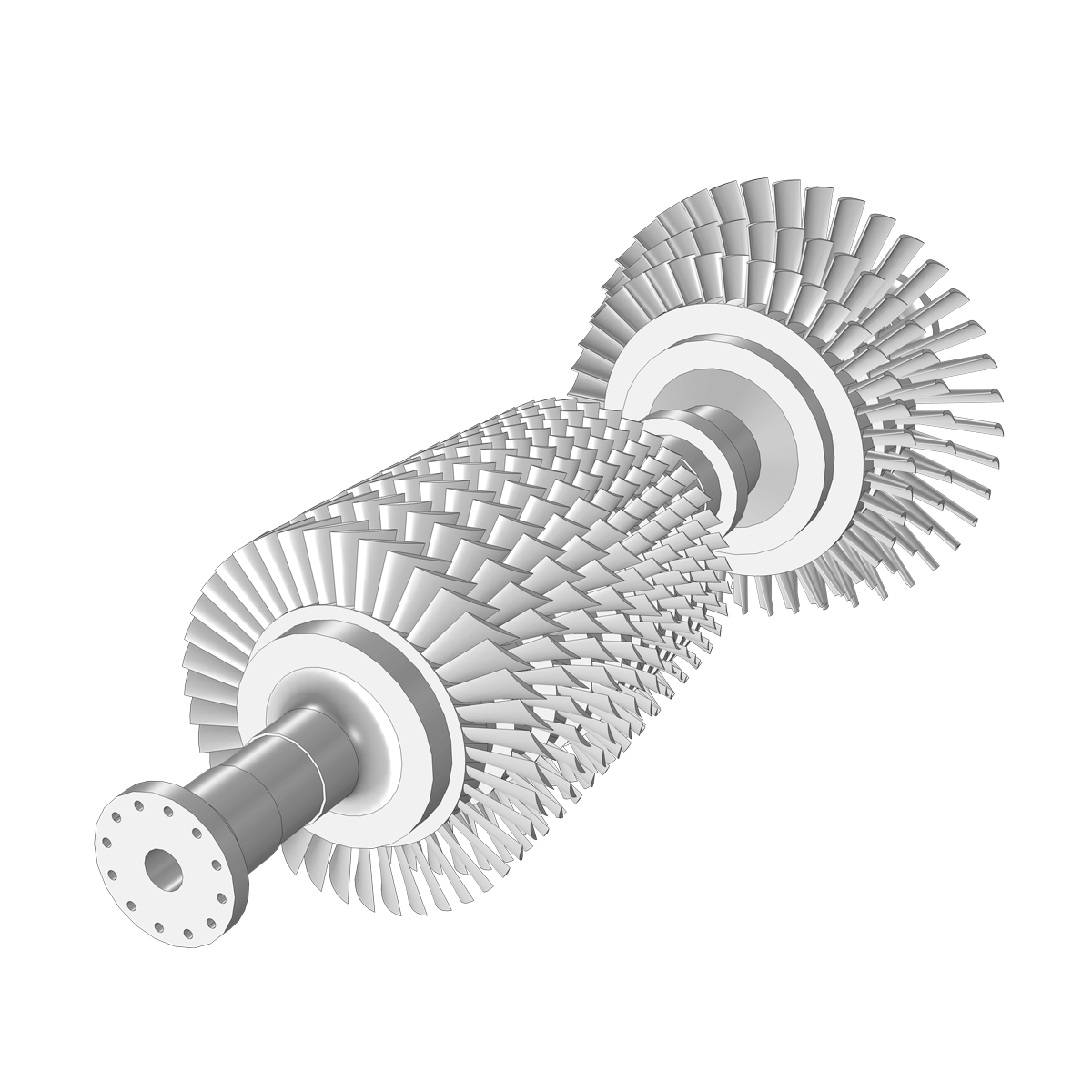
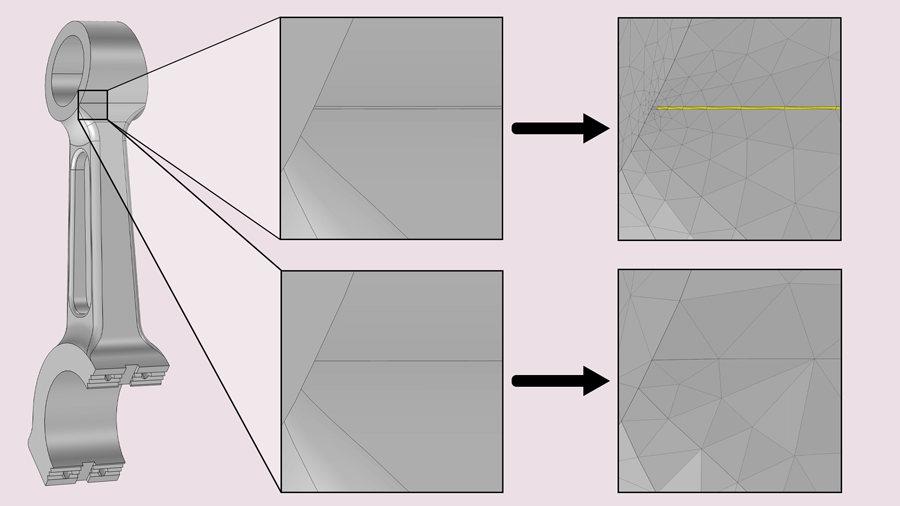
The CAD Import Module provides tools to ensure a smooth transition of a geometry from a CAD software to your COMSOL Multiphysics® analysis, which is perfect for a CAE engineer who does not have access to the CAD program. If you are a CAD user who is looking for a CAE tool, the LiveLink™ products from COMSOL provide additional functionality to connect your CAD system directly with COMSOL Multiphysics®. The synchronisation feature in the LiveLink™ products automatically updates the geometry in one program when changes are made in the other. With the LiveLink™ products, you avoid the import/export and reimporting of the entire CAD geometry when you want to make changes for further analysis. Additionally, parametric sweeps can automatically be run based on a geometric entity such as the length of an edge, and you can even run analyses to optimise the CAD geometry based on result parameters.
The list of current products that contain this functionality are as follows:
All trademarks listed herein are the property of their respective owners, and COMSOL AB and its subsidiaries and products are not affiliated with, endorsed by, sponsored by, or supported by those trademark owners. For a list of such trademark owners, see http://www.comsol.com/tm.
In order to fully evaluate whether or not the COMSOL Multiphysics® software will meet your requirements, you need to contact us. By talking to one of our sales representatives, you will get personalised recommendations and fully documented examples to help you get the most out of your evaluation and guide you to choose the best license option to suit your needs.
Fill in your contact details and any specific comments or questions, and submit. You will receive a response from a sales representative within one business day.